A single misplaced digit can derail a claim. Learn the essential codes, procedures, and best practices to ensure accurate billing for non-invasive cardiology services.
Coding is more than just data entry; it's the financial backbone of healthcare. A single misplaced decimal or an outdated code can lead to thousands of dollars in lost revenue. This is especially true in a complex specialty like cardiology. Getting cardiography coding right is essential for everything from patient bills and insurance coverage to the overall health of your healthcare revenue cycle management.
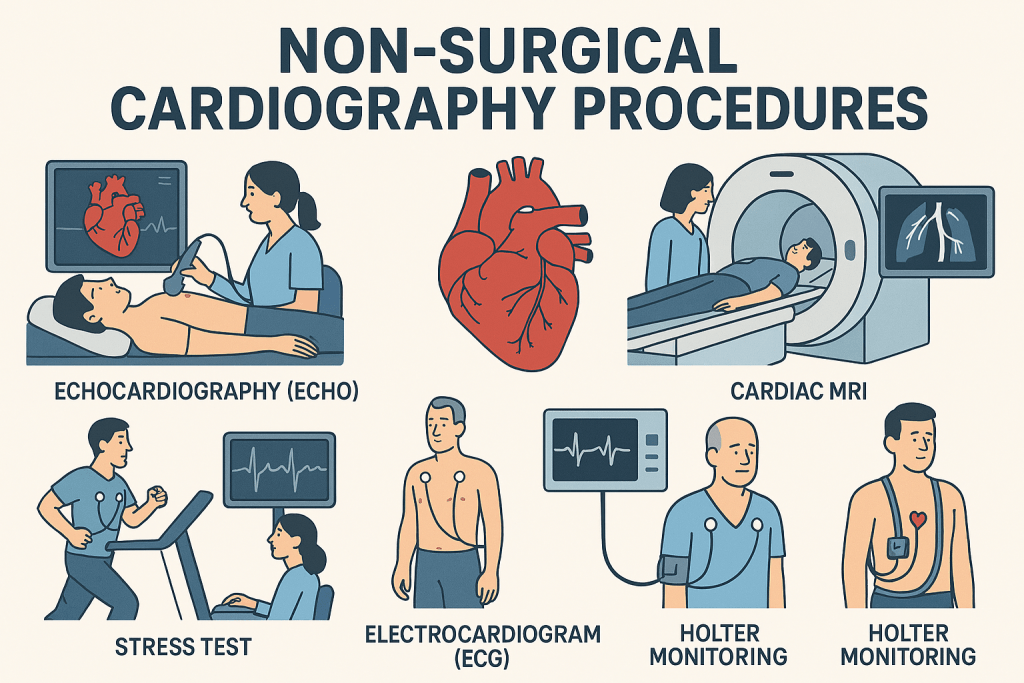
What Exactly is Non-Surgical Cardiography?
Non-surgical cardiography refers to a range of heart-imaging and heart-monitoring tests performed without a surgical incision. These tests allow doctors to observe how the heart is functioning, laying a critical foundation for diagnosing or managing various heart conditions without invasive procedures.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore some of the most common non-surgical cardiography procedures you'll encounter in cardiology coding. Understanding these tests in advance is the first step toward making your coding process smoother and more accurate.
How Cardiology Coding Works: The Process
Cardiology procedures are primarily coded using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes in the U.S. These codes, maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA), describe a wide range of medical, surgical, and diagnostic services. For inpatient services or in certain international contexts, the ICD-10-PCS system may also be used. For most outpatient non-surgical cardiography services, CPT is the primary system.
Procedure Performed
A non-invasive test like an ECG is conducted.
Documentation
The physician documents the procedure and findings.
Code Selection
The coder selects the correct CPT and ICD-10 codes.
Claim Submission
The coded claim is submitted to the payer.
Reimbursement
The claim is processed and paid (if coded correctly!).
Non-Surgical Cardiography Procedures in Detail
To help you navigate the coding landscape, we've compiled a detailed table of common non-surgical cardiography procedures, including their purpose and the relevant CPT and ICD-10-PCS codes. This serves as a quick-reference guide for your daily coding needs.
| Procedure | Purpose | CPT Codes | ICD-10-PCS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) | Detect arrhythmias, ischemia, heart attacks | 93000, 93005, 93010 | 4A02X4Z |
| Holter Monitor | Detect intermittent arrhythmias over 24–48 hrs | 93224, 93225, 93226, 93227 | 4A02X4Z |
| Event Monitor (Loop Recorder) | Long-term rhythm monitoring | 93268, 93270, 93271 | 4A02X4Z |
| Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) | Evaluate heart valves, function, and structure | 93306, 93307, 93308 | B245ZZ3 |
| Stress Tests (Exercise or Pharmacologic) | Assess heart function during stress | 93015, 93016, 93017, 93018 | B245ZZ3 |
| Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring | Assess calcium buildup for CAD risk | 75571 | B210YZZ |
| Cardiac MRI | Visualize heart structure and function | 75557, 75559, 75561 | B030ZZZ |
Dive Deeper: Common Procedures and Codes
Let's explore the most common non-invasive heart tests and their associated codes in a more interactive format. Each procedure has its own set of rules and codes, which are crucial to know for accurate billing.
What it is: A quick, painless test that records the heart’s electrical activity using electrodes placed on the skin.
Why doctors order it: To detect arrhythmias, ischemia, and signs of a recent or ongoing heart attack.
CPT Codes:
- 93000: Complete (includes both tracing and interpretation)
- 93005: Tracing only
- 93010: Interpretation only
ICD-10-PCS: 4A02X4Z – Monitoring of cardiac rhythm, external.
What it is: A portable device that continuously records heart rhythms for 24–48 hours.
Why doctors order it: To identify irregular heartbeats that may not appear during a standard ECG.
CPT Codes:
- 93224: Full service (global)
- 93225: Device hookup and patient instructions
- 93226: Technical recording and monitoring
- 93227: Final interpretation and report
ICD-10-PCS: 4A02X4Z – Monitoring of cardiac rhythm, external.
What it is: A heart ultrasound using a probe on the chest wall.
Why doctors order it: To evaluate heart valves, muscle function, chamber size, and ejection fraction.
CPT Codes:
- 93306: Complete echocardiogram with Doppler and color flow
- 93307: Complete echocardiogram without Doppler
- 93308: Limited or follow-up study
ICD-10-PCS: B245ZZ3 – Ultrasonography of heart, transthoracic, real-time.
What it is: Measures heart response to stress from exercise or medication. Stress echocardiography combines this with ultrasound imaging.
Why doctors order it: To detect ischemia or reduced blood flow in patients with symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath.
CPT Codes for Stress Tests:
- 93015: Complete stress test with supervision, interpretation, and report
- 93016: Supervision only
- 93017: Tracing only
- 93018: Interpretation and report only
CPT Codes for Stress Echo:
- 93350: Echocardiographic imaging during stress
- 93351: Full package: stress echo with supervision, interpretation, and report
ICD-10-PCS: B245ZZ3 – Transthoracic ultrasonography with stress.
What they are: Advanced imaging techniques. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring measures calcium buildup. Cardiac MRI provides highly detailed images of heart structure and function.
Why doctors order them: For risk assessment (calcium scoring) or to detect scarring, structural abnormalities, and defects (MRI).
CPT Codes:
- 75571: Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
- 75572-75574: Cardiac CT Angiography (CCTA)
- 75557-75565: Cardiac MRI codes
ICD-10-PCS:
B210YZZ: Cardiac CT without contrastB030ZZZ: Cardiac MRI
Common Mistakes in Cardiography Coding and How to Avoid Them
Even with a clear understanding of procedures, coders can fall prey to common errors. Let’s review some of the most frequent mistakes and provide actionable tips for prevention.
❌ Using the Wrong or Old CPT Codes
Using outdated codes or a global code when only part of the service was rendered is a frequent source of denials.
How to avoid?
- Always consult the latest CPT code book.
- Be precise: use modifiers like -26 for professional (interpretation) services or -TC for technical (testing) components.
❌ Not Matching the Right ICD-10 Diagnosis Code
A correct procedure code is useless if the diagnosis code doesn't justify the medical necessity of the test.
How to avoid?
- Use specific ICD-10 codes that clearly explain the reason for the test.
- Check payer-specific rules and resources like Medicare’s LCD/NCD lists for coverage guidelines.
❌ Billing for Procedures That Are Already Bundled
Unbundling procedures that are typically paid as a single service leads to denials and potential audits.
How to avoid?
- Check the NCCI edits to see if two services are bundled.
- If services were truly separate, use a modifier like -59 and ensure documentation supports it.
❌ Misusing or Forgetting Modifiers
Modifiers are crucial for telling the full story of a service. Forgetting them can lead to underpayment or denials.
How to avoid?
- Understand when to use common modifiers like -26, -TC, and -59.
- Always ensure the provider's notes clearly support the use of any modifier.
Quick Checklist for Easy and Accurate Cardiography Coding
Use this checklist as a final review before submitting a claim to reduce billing mistakes and speed up reimbursement.
Know the Test: Understand if it’s a diagnostic, monitoring, or imaging test. Each type has distinct coding requirements.
Use the Right CPT Code: Double-check that you're using the latest, most specific CPT code that matches the service provided.
Match CPT with the Right ICD-10: Avoid general diagnosis codes. The ICD-10 code must clearly demonstrate medical necessity.
Use Modifiers Correctly: Apply modifiers like -26, -TC, or -59 only when documentation fully supports their use.
Watch for Bundled Services: Consult NCCI edits to prevent unintentional unbundling and use modifier -59 only when services are truly distinct.
Check Insurance Rules: Payer policies vary. Always review specific coverage rules before billing to avoid surprises.
Document Everything Clearly: Ensure provider notes are comprehensive, explaining what was done, why it was necessary, and who performed each part of the test.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a CPT code and an ICD-10 code?
A CPT code describes the medical service or procedure performed, like an ECG. An ICD-10 code describes the patient's diagnosis, condition, or reason for the visit, justifying the medical necessity of the procedure. For more on CPT codes, check out our guide: CPT Codes in Medical Billing: Why It's Important.
How can I avoid claim denials in cardiology?
To avoid denials, focus on accuracy. Ensure your codes match the documentation, use the correct modifiers, and verify that the diagnosis code supports the procedure. Our healthcare denial management services page has more tips on this.
What is a Holter monitor and how is it coded?
A Holter monitor is a portable device that records heart activity for 24-48 hours. It's used to detect intermittent arrhythmias. You'll typically use CPT codes 93224-93227, depending on whether you're billing for the global service, technical component, or professional interpretation.
When should I use a modifier like -26?
You should use the -26 modifier when you are only billing for the professional component of a service, which is the physician’s interpretation and report. The technical component (the actual performance of the test) would be billed separately.
What is medical necessity in coding?
Medical necessity means that the procedure or service provided is reasonable and necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of a patient's illness or injury. A correct ICD-10 code provides this justification for the CPT code you bill.
Are ECGs and EKGs the same thing?
Yes, they refer to the same test. ECG stands for Electrocardiogram, and EKG comes from the German word "Elektrokardiogramm." Both are used interchangeably to describe the test that records the heart's electrical activity.
What is a stress echocardiogram?
A stress echocardiogram combines a stress test with an ultrasound of the heart before and after exercise. The CPT codes for a stress echo are different from a standard stress test and are generally found in the 93350-93351 range.
Why is it important to use specific ICD-10 codes?
Specific ICD-10 codes provide a clear and detailed clinical picture to the payer. Using a general code might not adequately justify the medical necessity of a procedure, which can lead to a denial. Precision is key for reimbursement.
What services are included in cardiology billing?
Cardiology billing includes a wide range of services, such as coding and billing for diagnostic tests, procedures, and office visits. For more information, you can visit our Cardiology Billing Service page.
What are NCCI edits?
NCCI stands for National Correct Coding Initiative. These are a set of rules from CMS that prevent improper coding and billing of services. They often dictate which procedures cannot be billed together on the same day unless specific modifiers are used.
How does medical credentialing relate to billing?
Medical credentialing is the process of verifying a healthcare provider's qualifications and getting them enrolled with insurance plans. If a provider isn't properly credentialed, their claims will be denied, so it's a critical first step to ensuring you can bill for services. Learn more on our FAQ page about physician credentialing.
What is a Holter monitor hookup service?
A Holter monitor hookup service, coded with CPT 93225, includes attaching the device to the patient and providing them with instructions on how to use it. This is typically billed by the provider who physically performs this part of the service.
Can a provider get help with their medical billing?
Yes, many providers outsource their billing to a service like RxCredentialing to increase efficiency and reduce errors. Our page on medical billing for small practices explains the benefits.
What is revenue cycle management?
Revenue cycle management (RCM) is the entire process of managing claims, payments, and revenue generation from the moment a patient schedules an appointment to the final payment. Proper coding is a key part of RCM. We have a detailed guide on revenue cycle management in healthcare.
What is a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)?
A TTE is a common type of heart ultrasound where a technician places a probe on the patient's chest to create images of the heart's structure and function. It's often coded with CPT 93306.
How do I bill for a cardiac CT for calcium scoring?
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring is a non-invasive scan to measure calcium buildup in the heart arteries. The specific CPT code for this service is 75571.
What happens if a claim is denied?
If a claim is denied, it must be addressed and resubmitted with the correct information. The denial reason will be provided by the payer, and you will need to appeal or correct the claim accordingly. Our services can help with AR recovery and managing these issues.
Why is it important to stay up to date on codes?
CPT and ICD-10 codes are updated annually. Using outdated codes will almost always result in claim rejections. Staying current is essential for accurate reimbursement.
How do I know which modifier to use?
The choice of modifier depends on the specific circumstances of the service provided, such as whether it was a professional component, a technical component, or a distinct procedural service. Always refer to official coding guidelines and the provider's documentation.
What is the role of a medical billing service in cardiology?
A medical billing service for cardiology handles all aspects of the billing cycle, including claim submission, denial management, and accounts receivable follow-up. This frees up the practice to focus on patient care. You can find more details on our website about cardiology billing services.
Conclusion
Non-surgical cardiography procedures may be less invasive for the patient, but coding them requires the same level of precision and detail as any surgical procedure. By understanding the common non-invasive tests—from ECGs and stress tests to advanced heart scans—and mastering the associated CPT and ICD-10-PCS codes, you can significantly improve your practice's billing accuracy.
Using the right codes, matching them with a specific diagnosis, and applying the correct modifiers makes a huge difference in getting paid on time and avoiding claim rejections. Good coding benefits everyone: it helps patients with accurate billing, allows doctors to be reimbursed for their work, and keeps the cardiology billing team on track. With this knowledge, you are well-equipped to streamline your process, reduce errors, and ensure a healthier revenue cycle.