In the United States, over 6.5 million patients suffer from chronic wounds annually, making accurate billing for wound care services more crucial than ever. For healthcare providers and medical billing teams, even a small coding error can result in costly denials and delayed reimbursements. One of the most frequently misunderstood and denied codes in this area is CPT code 97598.
If your practice routinely handles debridement procedures, understanding this code is essential to maintaining healthy revenue cycles. In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about CPT 97598, from clinical use cases and modifier application to proper documentation and reimbursement tips.

What Is CPT Code 97598?
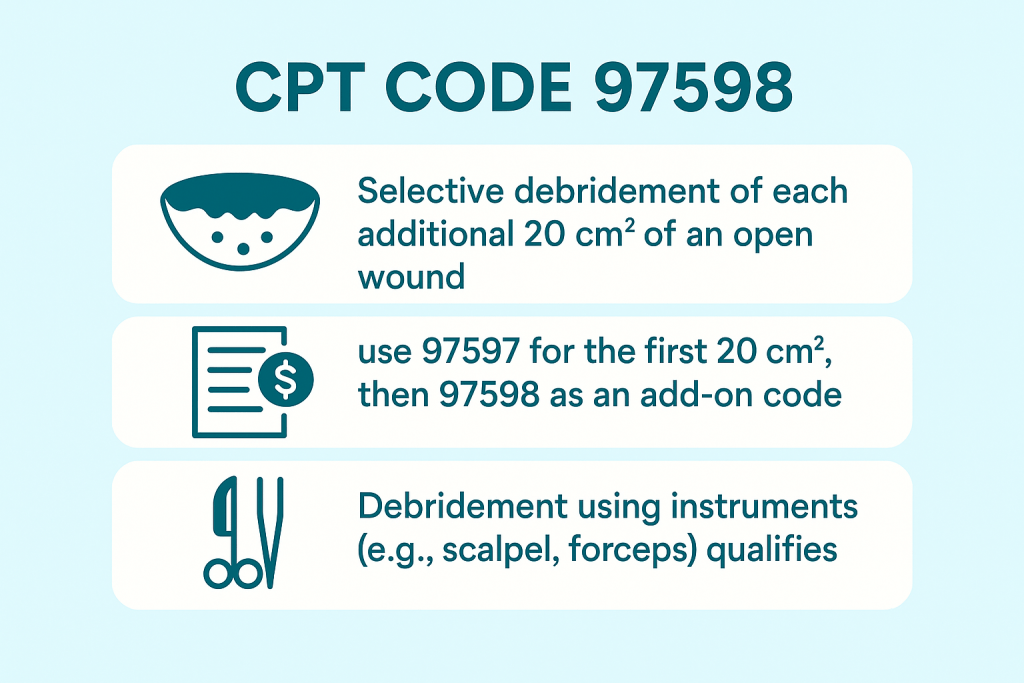
CPT code 97598 is used for selective debridement of open wounds, each additional 20 square centimeters (cm²) beyond the first 20 cm². The initial 20 cm² is billed using CPT code 97597, and 97598 is added for any remaining wound area in 20 cm² increments—or any portion thereof.
🧠 Example: A patient presents with two wounds totaling 50 cm². You would bill 97597 for the first 20 cm², and then two units of 97598 for the remaining 30 cm² (20 + 10 cm²).
Important to note:
- CPT 97598 is an add-on code and must be billed with 97597.
- The procedure must involve selective removal of necrotic tissue using tools like scalpels, scissors, or high-pressure water jets.
- Basic wound cleansing or removal of secretions does not qualify.
When Should You Use CPT Code 97598?
CPT 97598 applies in several wound care scenarios, including:
🩺 Post-Surgical Wound Complications
Surgical wounds can become infected or necrotic, requiring aggressive tissue removal to promote healing. For wounds exceeding 20 cm², CPT 97598 becomes necessary.
🦶 Diabetic Foot Ulcers
These chronic wounds often demand extensive debridement. If the ulcer is 35 cm², for example, bill 97597 for the first 20 cm² and 97598 for the remaining 15 cm².
For more information on related services, see our podiatry medical billing services or billing for physical therapy.
Proper Use of Modifiers with 97598
Modifiers help clarify services and support payment. Here are the most common ones for CPT 97598:
| Modifier | Description | When to Use It |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | Increased procedural services | Use when treatment is significantly more complex |
| 59 | Distinct procedural service | For procedures on separate anatomical sites |
| XS | Separate structure | Used for a different organ/structure on same date |
| XU | Unusual non-overlapping service | For unrelated procedures performed on the same day |
| 76 | Repeat procedure by same provider | For same-day repeat procedures |
| 77 | Repeat procedure by another provider | Used if another provider repeats the procedure |
⚠️ Tip: Modifier 59 is frequently misused and often leads to denials. Only apply it if wounds are genuinely distinct and on different anatomical sites.
Need help handling modifiers? Our team specializes in accurate insurance credentialing services and billing support to minimize errors and maximize revenue.
Documentation Requirements for CPT 97598
Proper documentation is non-negotiable. Make sure your medical records include:
- Wound size (length, width, and depth)
- Type of necrotic tissue removed
- Debridement method used
- Clinical justification and medical necessity
- Progress notes tracking wound healing over time
For facilities dealing with complex billing documentation, consider leveraging our virtual medical assistant services.
Reimbursement Guidelines for CPT 97598
Reimbursement varies based on MAC locality and facility type. However, the national average Medicare reimbursement is:
- $43.34 in non-facility settings
- $23.29 in facility-based settings
🔎 Check your local rates using CMS’s PFS Look-Up Tool.
Clean Claims Checklist for CPT 97598
- ✅ Measure the wound accurately
- ✅ Use CPT 97597 as the primary code
- ✅ Add 97598 in 20 cm² increments beyond the first 20 cm²
- ✅ Attach appropriate modifiers when required
- ✅ Ensure thorough documentation supports the procedure
- ✅ Verify patient’s insurance eligibility using our eligibility verification services
CPT code 97598 can be a revenue booster—or a compliance pitfall—depending on how it’s used. With accurate wound measurements, supporting documentation, and the correct coding sequence, you can reduce denials and ensure fair reimbursements.
If you’re still facing issues, RxCredentialing is here to help. From wound care billing to mental health billing services, our end-to-end medical billing solutions ensure your claims go through the first time.
💡 Related Reading:
- How to Credential with Aetna (2025)
- Mastering CAQH Credentialing
- Easy Guide to Modifier Q8
- What Is Medicare Jurisdiction L (JL)?
For further questions or support, contact us at RxCredentialing.com — your partner in compliance, credentialing, and clean claims.
CPT Code 97598 – Frequently Asked Questions
It’s used for selective debridement of wounds beyond the first 20 cm². It’s always billed with CPT 97597.
No, CPT 97598 is an add-on code and must be billed with CPT 97597.
Bill CPT 97597 for the first 20 cm² and one unit of 97598 for each additional 20 cm² or fraction thereof.
Yes, diabetic ulcers often exceed 20 cm² and require debridement, making CPT 97598 applicable.
Common ones include 22, 59, XS, XU, 76, and 77, depending on clinical context.
Include wound measurements, tissue removed, method used, and medical necessity in the record.
Rates vary, but the national average is around $43.34 (non-facility) and $23.29 (facility).
Yes, as long as the total wound area justifies additional units and the wounds meet clinical criteria.
Scalpels, scissors, forceps, curettes, and waterjets qualify. Basic wound cleansing does not.
Yes. Virtual medical assistants help streamline documentation and reduce coding errors that lead to denials.