Struggling with CPT 97602 claim denials? You’re not alone. Non-selective debridement claims are one of the most rejected in wound care billing.
Why? Misunderstanding the documentation requirements and incorrect code usage are to blame.
In this definitive guide, our billing experts break down CPT Code 97602, clarify common mistakes, and show you how to optimize claims submission to avoid costly denials.
✅ Pro Tip: If your practice is overwhelmed by rejected claims or documentation bottlenecks, explore professional medical billing services for small practices that can take the stress out of wound care billing.
🔎 What is CPT Code 97602?
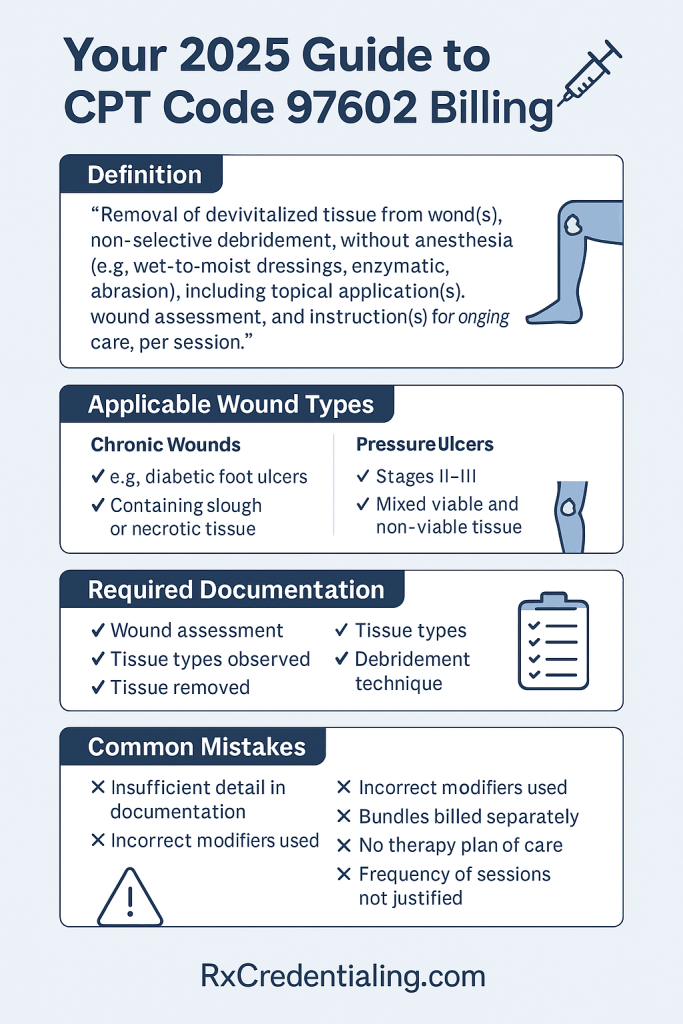
97602 is defined as:
“Removal of devitalized tissue from wound(s), non-selective debridement, without anesthesia (e.g., wet-to-moist dressings, enzymatic, abrasion), including topical application(s), wound assessment, and instruction(s) for ongoing care, per session.”
Let’s simplify it.
CPT 97602 represents non-selective wound debridement, which removes both healthy and dead tissue without anesthesia. Unlike selective methods, this approach uses mechanical, enzymatic, or abrasive techniques and is often applied when the distinction between viable and non-viable tissue isn’t possible.
It’s often dubbed the “Sometimes Therapy Code” because it may or may not require a therapy plan of care depending on the provider.
💡 Learn how credentialing for nurse practitioners plays a key role in submitting compliant claims under 97602.
🩹 Techniques Included Under 97602
- Wet-to-moist dressings (mechanical removal during dressing changes)
- Enzymatic debridement using agents like collagenase
- Gentle abrasion or irrigation to remove slough and necrosis
- Whirlpool therapy
Note: Anesthesia is not included. If used, bill it separately with appropriate anesthesia CPT codes.
📋 When Should You Use CPT 97602?
✅ Chronic Wound Management
Example: Diabetic foot ulcers with slough and necrotic tissue
Best method: Enzymatic or wet-to-moist dressings
Billing code: CPT 97602
✅ Pressure Ulcers
Example: Stage II or III pressure ulcers with mixed tissue
Billing challenge: Distinguishing selective from non-selective debridement
Solution: Confirm method with the physician, and document accordingly.
For added peace of mind, our physician billing services can help ensure all coding is accurate and reimbursable.
🧾 Modifiers for CPT 97602
| Modifier Type | Code | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomical | LT / RT | Left / Right side | Use based on wound location |
| Finger | F1–F9 / FA | Finger location | If wound is on fingers |
| Toe | T1–T9 / TA | Toe location | If wound is on toes |
| Procedural | 59 | Distinct procedural service | Multiple sessions on the same day |
💰 Billing & Reimbursement Guidelines
🚫 Medicare Status Indicator “B”
This means CPT 97602 is bundled under Medicare and not reimbursed separately unless billed by therapists with valid therapy modifiers.
📑 Documentation Requirements
Include the following:
- Detailed wound assessment (with measurements)
- Debridement technique used (e.g., enzymatic)
- Tissue types and amount removed
- Patient’s response to treatment
- Ongoing wound care instructions
📎 Need support? Check out our insurance eligibility verification services to ensure proper pre-auths and claims acceptance.
🚫 Common CPT 97602 Mistakes
- Missing or vague documentation
- Incorrect or missing modifiers
- Filing under the wrong provider type
- Forgetting to justify frequency of treatment
- Billing anesthesia without a separate code
✅ Final Thoughts
Over 6.5 million Americans suffer from chronic wounds annually. Denials for CPT 97602 can hurt practice cash flow. By mastering correct billing procedures and documentation, you can turn around denial rates and boost reimbursement.
Still unsure? Work with the pros. Our team at RxCredentialing.com offers comprehensive services including telehealth credentialing for counselors, mental health billing services, and more.




